

Warfarin site: NSAIDs, Sulfonamides, Phenytoin, Bilirubin.ī. Ø Especially, the acidic drugs (salicylates, vitamin C, sulfonamides, barbiturates, penicillin, tetracyclines, warfarin, probenecid, etc.) are bound to albumin.Ī. Ø The most important protein (59% of total) that binds the drugs in blood is albumin for most of the drugs. Ø It allows temporary drug storage, and reduces the elimination. Ø Protein-bound drugs do have not any therapeutic effects. Ø Drug that reaches the blood interact with plasma proteins and bind with them. Ø The total concentration of a drug increases faster in well-perfused organs. Ø S kin, resting skeletal muscle, and bone have a low perfusion rate. Ø Kidney, liver, brain, and heart have a high perfusion rate (ml/100 g tissue/min) in which the drugs distribute higher Ø There is a positive correlation between the blood flow in the tissue and the distribution of the drugs. Ø Some drugs tend to be concentrated in particular tissues. Ø There is a positive correlation between the diffusion rate of the drug and the distribution rateī) The Affinity of the Drug to the Tissue Components : N.B: The drugs which are given intravenously can be distributed faster rate.FACTORS AFFECTING THE DISTRIBUTION OF DRUGS The drug which are smaller and can be passed with water like urea, alcohol etc, can be diffused through capillaries into the ECF but lipid soluble drugs can be diffused at a faster rate & Dv is more in the ECF. Ex- Sulfate distributed in about 22% of body weight extra cellularly. The volume of distribution of these substances vary considerably. Insulin, Sucrose, thiosulfate, sulfate, chloride, bromide & sodium belongs to this class.
#PASSAGE OF DRUGS INTO VARIOUS BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS FREE#
The drug molecules are present in this type of body compartment of fluid as free & bound form.The fluid also present as a transcellular form, present in the cavities made up of cells like CSF, Intra ocular fluid (IOF), Pleural, Peritoneal, Synovial, Digestive secretions etc, This type of fluid is produced by the cells present nearby to that organ.O Extracellular fluid (ECF) - ECF involves blood plasma, interstitial fluid, & lymph. O Intracellular fluid (ICF) - It involves the fluid present in the cells of the body. Mainly body fluid is distributed in body into 2 compartments.Adipose tissue contains no water, thus fatty persons have low volume of water.It is gradually more in men(60%) then women ( 55%) ,The infants have the highest % of water upto 75 % of body weight.Around 45 to 75% of the body weight, water is present in the body.Body fluid means water and its dissolved solvent.The lipid solubility and pH difference between two compartments is also important for movement of drug from blood to tissue.The drug can be moved easily from blood to tissue because of higher vascular permeability of capillary epithelium except brain.The drug, for reaching the low perfused organs takes more time (Up to many hours) but it is necessary because the large mass fraction is present in low perfused area because of having more amount in body than higher perfused one.The drug can be moved from the plasma to the tissue until the equilibrium is established (for unbound drug present in plasma).Table of content Factors Affecting Distribution Of drug The drug is easily distributed in highly perfused organs like liver, heart, kidney etc in large quantities & in small quantities it is distributed in low perfused organs like muscle, fat, peripheral organs etc. The lipid solubility, pH of compartment, extent of binding with plasma protein and tissue proteins,cardiac output, regional blood flow, capillary permeability are associated for distribution of the drug trough tissues.
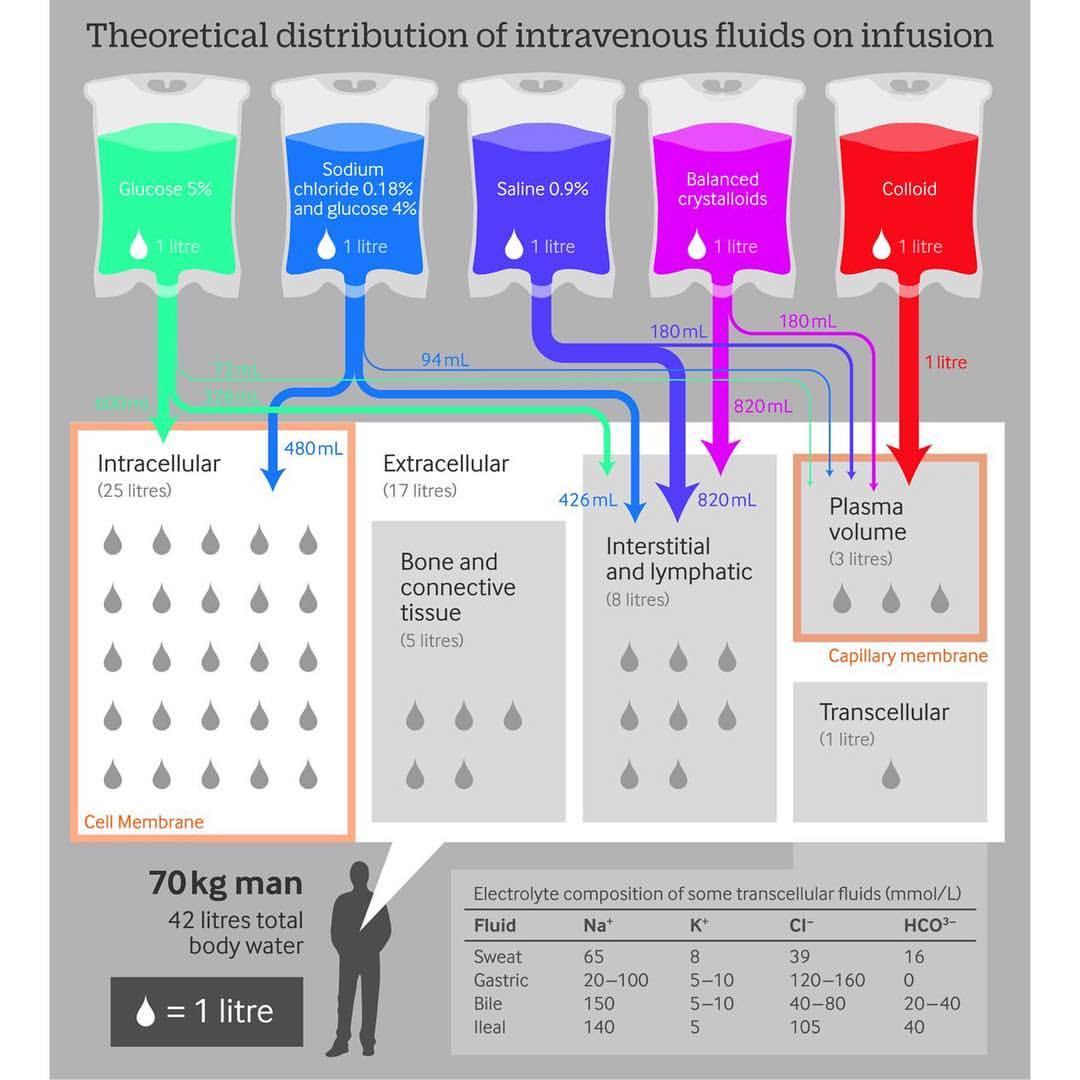
Once a drug enters into systemic circulation by absorption or direct administration, A drug has to be distributed into interstitial and intracellular fluids.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
